exploitedworkerbee
Quiet Quitting Mod
he’s a real gemThat doesn't include the "contributions" removed by exploitedworkerbee.....
he’s a real gemThat doesn't include the "contributions" removed by exploitedworkerbee.....
Mine processed through isc Los Angeles today. I’m unclear if that means it has cleared customs or is in the process of that. Since it disappeared for two weeks I wonder if it didn’t come by boatI got an LZ tracking number from Christmas promo (international)
12/23 - payment cleared
12/30 - tracking received (asked for it)
01/07 - airline departure
01/08 - plane arriving
01/16 - airline departure
01/16 - plane arrives at port
01/21 - at local USPS distribution center
Should get in next couple of days!
You specifically were called a dumb shit, then a follow up post had a similar sentiment for the rest of us.Awwww I missed @shieldzz reply. Guess it was deleted before an email was sent. Anyone catch it? I wanna know how I was insulted this time.
For the record, I was the only person to respond kindly to him on his first posts, I'm not just being a bitch.
Thank you, I actually appreciate knowing! You were on the ball, I didn't even get an email yet. Just the phone notification that didn't tell me what was said.You specifically were called a dumb shit, then a follow up post had a similar sentiment for the rest of us.
I have, trying to look up GYC and HK peptides… it says no results when I use the*so frustrating😭Try putting an asterisk * after your search term.
If you Google search "glp-1 forum GYC" a couple threads come up. I think HK is very new (and possible a cut/paste sibling vendor) possibly little if any feedback.I have, trying to look up GYC and HK peptides… it says no results when I use the*so frustrating😭
Nope. Tracy said it will be sometime after Chinese New Year when they reappear.Has anyone seen or heard from QSC at all?
Tracy said it’ll be a few days like 2 weeks ago, not that it will be after CNY. I think QSC is donezo.Nope. Tracy said it will be sometime after Chinese New Year when they reappear.
I feel like I missed my rite of passage by missing out on ordering from them at least once.Tracy said it’ll be a few days like 2 weeks ago, not that it will be after CNY. I think QSC is donezo.
I mean, you told them what you wanted and paid your money and decent product showed up, eventually. If you want more than that you’re fuckedI feel like I missed my rite of passage by missing out on ordering from them at least once.
They might come back, but even if that happens I won’t be placing an order for a while until they demonstrate nothing has changed. It’s a good time to have a solid hoard.I feel like I missed my rite of passage by missing out on ordering from them at least once.
Wouldn't surprise me one bit. All good things must come to an endTracy said it’ll be a few days like 2 weeks ago, not that it will be after CNY. I think QSC is donezo.
I have all I want as far as sema/tirz/cagri. Most of the other things are wants, not needs.They might come back, but even if that happens I won’t be placing an order for a while until they demonstrate nothing has changed. It’s a good time to have a solid hoard.
You know I think I assumed that he meant after CNY, but you are right. When you look back at his post it says a "few days" and that was Jan 10th.Tracy said it’ll be a few days like 2 weeks ago, not that it will be after CNY. I think QSC is donezo.
We shall see. Despite being a newbie, I have an opinion about this: Tracy has been selling peptides for a long time and steroids before that. Tracy's reputation means a great deal. Yes, I know Tracy bad talks many folks, rubbing them the wrong way. However, Tracy also has a reputation for always delivering the stuff when paid. Tracy also has a reputation for producing general high quality stuff. Tracy has a reputation for honoring the representations made by Tracy. Tracy was likely the biggest seller of grey peptides. Tracy's reputation is worth too much for Tracy to simply disappear. In the world of grey, having a loyal base of past customers is extremely valuable. Unless Tracy is genuinely ready to retire or has gotten into some sort of trouble, for example, being incarcerated, there is too much money to be lost if Tracy doesn't come back. As to Tracy saying that that Tracy would be back in a few days, Tracy didn't quite say that; I posted exactly what Tracy said below. It is typical for things to be quiet during Chinese New Year. I still expect Tracy back. However, until my last order gets delivered, I won't be purchasing anything from Tracy. I've been happy with my SRY orders. I do recall at least one person, I believe in this forum, saying that a purchase made shortly before Tracy disappeared has arrived.Tracy said it’ll be a few days like 2 weeks ago, not that it will be after CNY. I think QSC is donezo.
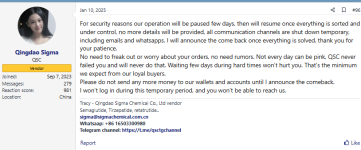
I feel like you said Tracy as many times as you could in an effort to summon them. Like Bloody Mary.We shall see. Despite being a newbie, I have an opinion about this: Tracy has been selling peptides for a long time and steroids before that. Tracy's reputation means a great deal. Yes, I know Tracy bad talks many folks, rubbing them the wrong way. However, Tracy also has a reputation for always delivering the stuff when paid. Tracy also has a reputation for producing general high quality stuff. Tracy has a reputation for honoring the representations made by Tracy. Tracy was likely the biggest seller of grey peptides. Tracy's reputation is worth too much for Tracy to simply disappear. In the world of grey, having a loyal base of past customers is extremely valuable. Unless Tracy is genuinely ready to retire or has gotten into some sort of trouble, for example, being incarcerated, there is too much money to be lost if Tracy doesn't come back. As to Tracy saying that that Tracy would be back in a few days, Tracy didn't quite say that; I posted exactly what Tracy said below. It is typical for things to be quiet during Chinese New Year. I still expect Tracy back. However, until my last order gets delivered, I won't be purchasing anything from Tracy. I've been happy with my SRY orders. I do recall at least one person, I believe in this forum, saying that a purchase made shortly before Tracy disappeared has arrived.
View attachment 5310
I was trying to avoid using a pronoun, therefore, I repeatedly said Tracy.I feel like you said Tracy as many times as you could in an effort to summon them. Like Bloody Mary.
Which one is Tracy?
I won't burn my favorite peptides. Maybe my nonfavorites.I know how it sounds, but maybe if we all build a little shrine to Tracy and burn some of our favorite peptides on a tiny altar before her image, she'll come back. Just a thought.
i'll leave that up to imagination 😉Which one is Tracy?
Well the guy in the back is definitely Winty.Which one is Tracy?
We shall see. Despite being a newbie, I have an opinion about this: Tracy has been selling peptides for a long time and steroids before that. Tracy's reputation means a great deal. Yes, I know Tracy bad talks many folks, rubbing them the wrong way. However, Tracy also has a reputation for always delivering the stuff when paid. Tracy also has a reputation for producing general high quality stuff. Tracy has a reputation for honoring the representations made by Tracy. Tracy was likely the biggest seller of grey peptides. Tracy's reputation is worth too much for Tracy to simply disappear. In the world of grey, having a loyal base of past customers is extremely valuable. Unless Tracy is genuinely ready to retire or has gotten into some sort of trouble, for example, being incarcerated, there is too much money to be lost if Tracy doesn't come back. As to Tracy saying that that Tracy would be back in a few days, Tracy didn't quite say that; I posted exactly what Tracy said below. It is typical for things to be quiet during Chinese New Year. I still expect Tracy back. However, until my last order gets delivered, I won't be purchasing anything from Tracy. I've been happy with my SRY orders. I do recall at least one person, I believe in this forum, saying that a purchase made shortly before Tracy disappeared has arrived.
 www.sigmachemical.com.cn
www.sigmachemical.com.cn
Tracy is a smart cookie and surely knew the gig wasn’t forever. Eventually ends in retirement or jail. If I were him, assuming he got a healthy cut of those millions and the Chinese operation got stung by the authorities there, I’d probably just call it good and move on. I know this is a lot of assumptions with little evidence but it’s why I’m thinking we won’t see them again in any recognizable form.Their website is expired.
Wholesale lighting tower, Construction machinery Suppliers -Equipment
As one of the most professional Intelligent Technologies(Shandong) Co.Ltd suppliers, China Equipment Intelligent Technologies(Shandong) Co.Ltd experts in manufacturing and Exporting lighting tower, Construction machinery in wholesale pricewww.sigmachemical.com.cn
Chinese law enforcement is notoriously corrupt. If I had to read between the lines, it sounded like they were renegotiating their "look the other way" fees. But then their website expiration is a bad sign that perhaps they're shuttering their doors.
I assumed that a few days meant they were taking off early for CNY.
Only time will tell.
If Tracy doesn't come back, I'm sure components of QSC will reform and regroup into a new fake entity and show up on the scene shortly after CNY.
